

ID is the pull request id and BRANCHNAME is the name of the branch that you want to create. You can use git fetch command as follows to achieve this. fetching a remote PR (Pull Request) in to local repoįor purposes of reviewing and such, PRs in remote should be fetched to the local repo. If you look out for the words git pull but don’t see them, look for the word sync instead. git pull in IDEsĬommon language in other IDES may not include the word pull. Whenever you checkout to another branch that may have new changes, it’s always a good idea to execute git pull. But, this means that if you are checked out to feature branch and you execute git pull, when you checkout to master, any new updates will not be included. Using git pull, you get both parts of these updates. git merge updates the current branch with the corresponding remote tracking branch. Git fetch updates remote tracking branches. Without any arguments, git merge will merge the corresponding remote tracking branch to the local working branch. No changes are actually reflected on any of the local working branches. On its own, git fetch updates all the remote tracking branches in local repository.

Git pull is a combination command, equal to git fetch + git merge.
#Git pull remote branch updates update
Every time you execute git pull or git fetch commands, you update remote tracking branches. With remote tracking branches, you can work in Git on several branches without network interaction. The information in the remote tracking branches reflects the information from that interaction.) ( When was the last network interaction that would have brought information locally? Remember when this information was last updated.
#Git pull remote branch updates code
These are read-only copies of the code as it appears on the remote. If you execute git branch -all within a Git repository, remote tracking branches appear in red. To keep track of this, Git uses something called remote tracking branches. And, different copies of the same branches on every developer’s computer and on the remote. There are different versions of the same file on each branch. When working with Git, it can feel like there are lots of copies of the same code floating all over the place. And, a remote repository has no awareness of local changes until commits are pushed. A local repository has no awareness of changes made on the remote repository until there is a request for information. There are only four commands that prompt network interactions in Git. After pushing code up to the shared remote repository, other developers can pull changed code. With DVCS, developers can be working on the same file at the same time in separate environments. Git is a Distributed Version Control System (DVCS). If there is no remote tracking branch, Git doesn’t know where to pull information from. The branch you are currently checked out to has a corresponding remote tracking branch You might need to enter git pull origin or git pull upstream. If there are multiple remotes, git pull might not be enough information.The local repository has a linked remote repository (More information on remote tracking branches in the next section.)īut, there are a few things to keep in mind for that example to be true: Ex: While working locally on master, execute git pull to update the local copy of master and update the other remote tracking branches. Use git pull to update a local repository from the corresponding remote repository.
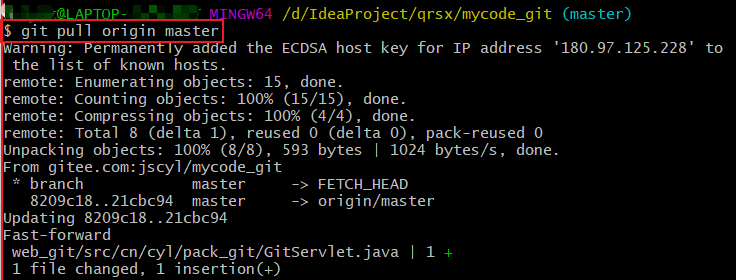
Thus, you should always commit your changes in a branch before pulling new commits from a remote repository. If you have uncommitted changes, the merge part of the git pull command will fail and your local branch will be untouched. BRANCH-NAME is the name of your branch.REMOTE-NAME is the name of your remote repository.REFSPEC specifies which refs to fetch and which local refs to update.You can read more about the different options in the Git documentation OPTIONS are the command options, such as -quiet or -verbose.This command’s syntax is as follows: # General format Git pull fetches ( git fetch) the new commits and merges ( git merge) these into your local branch. Updates the remote tracking branches for all other branches.Updates the current local working branch (currently checked out branch).It is one of the four commands that prompts network interaction by Git. Git pull is a Git command used to update the local version of a repository from a remote.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
